The diaphragm receives nerve innervation from the phrenic nerve which is made up from branches from the 3rd 4th and 5th cervical neck nerve roots. During normal expiration breathing out the diaphragm relaxes allowing the air to flow out as the lungs deflate similar to the way an inflated balloon deflates when released.
The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology Ii
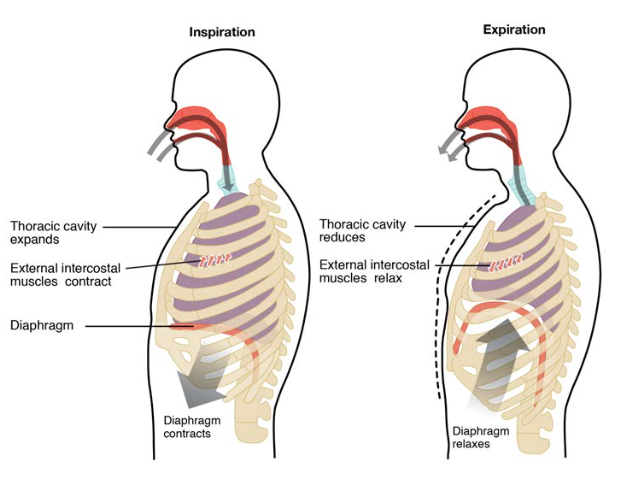
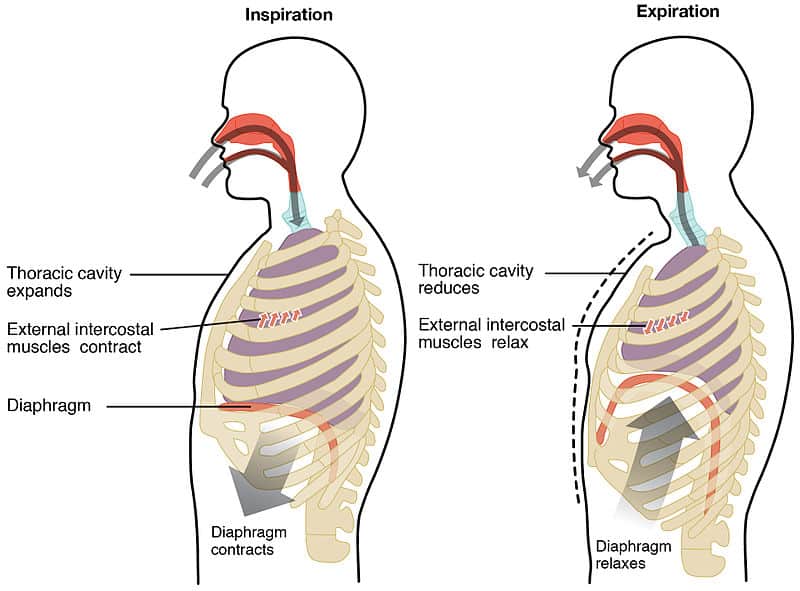
During quiet breathing the diaphragm and external intercostals muscles contract.

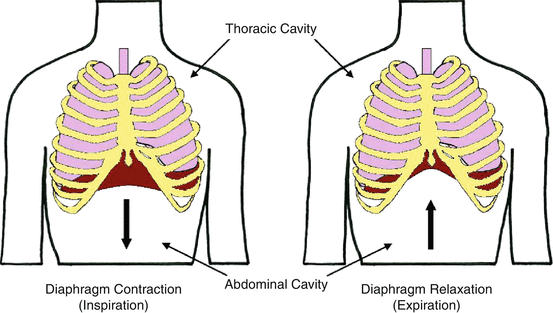
. Diaphragm relaxes to return to its resting position reducing the superiorinferior dimension of the thoracic cavity. Inhalation is the process of breathing inWhen you breath in the diaphragm contracts and moves downwards This makes the spaces in the chest to expand and lungs increases in sizeThe air then enters the lungs to minimise the pressure in the lungsThe external intercostal muscles contract making the ribs to move outwards and inwards and they help to. The diaphragm contracts and pulls downward while the muscles between the ribs contract and pull upward.
The diaphragm changes its electical charge and it becomes. This is an important muscle that. As the intercostal muscles relax and the thoracic cavity becomes smaller the intra-alveolar pressure INCREASES.
30 with plane of the plate. This will cause the air to move out expiration. Which describes the role of the diaphragm during inhalation.
Upon inhalation the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges. Both inhalation and expiration are mediated by voluntary and involuntary controls. During expiration relaxation of the diaphragm and external intercostals.
C the diaphragm moves up and down causing rapid swings in pressure in the thoracic cavity. During expiration the diaphragm relaxes and the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases. During INSPIRATION the intra-alveolar pressure is less than atmospheric pressure.
The diaphragm moves up and down causing rapid swings in pressure in the thoracic cavity. The intercostal muscles between the ribs relax causing the area of the chest cavity to reduce. A charged particle having charge.
The diaphragm contracts during inspiration and relaxes during expiration. Eventually the area in the chest reduces and carbon dioxide-rich air is. It is initiated by relaxation of the inspiratory muscles.
The diaphragm moves into the thoracic cavity and generates a positive pressure in the thorax relative to the atmosphere. When the diaphragm contracts the intra-alveolar pressure DECREASES. Diaphragm plays a very important role in the process of breathing.
During inhalation the diaphragm muscle contracts and this causes it to effectively move downwards its previously upwardly curving shape becomes a flatter one and this. The abdominal musclesalso aid expiration because when they contract they force abdominal organs up against the diaphragm and further decrease the volume of the thorax. The diaphragm flattens making the chest cavity larger and air flows in.
This contraction creates a vacuum which pulls air into the lungs. Diaphragm contracts during expiration. During expiration which best describes the role of the diaphragm.
Role of the upper airway muscles in respiration Without recapitulating the content of the upper airway anatomy chapter it will suffice to say that the upper airway muscles are at least as important as the diaphragm and chest wall because they maintain airway patency during inspiration. It is large dome-shaped muscle that contracts rhythmically and continually. C and mass of.
The diaphragm flattens making the chest cavity smaller and air is sucked in. Expiration is the phase of ventilation in which air is expelled from the lungs. During expiration the diaphragm moves to its original position and gradually moves the air outwards.
During expiration which best describes the role of the diaphragm. The diaphragm belongs to the Muscular and Respiratory systemsRespiratoryThe diaphragm is part of the respiratory systemThe diaphragm is a large dome-shaped muscle that plays an important role. For the diaphragm Poole et al 1997 is best though it is paywalled.
During forced expiration the internal intercostal musclesexcluding the interchondral part contract and depress the rib cage. Lets understand the function of diaphragm with the help of a diagram. The diaphragm moves upward making the chest cavity smaller and air is pushed out.
Upon exhalation the diaphragm relaxes and returns to its dome-like shape and is forced out of the lungs. Which statement best describes the diaphragms role in respiration. B the diaphragm changes its electrical charge and it becomes positive.
Contraction and expansion of the diaphragm helps in inhaling and exhaling air. The diaphragm is a sheet of internal muscle which extends across the bottom of the rib cage. During exhalation the diaphragm moves up and ribs move downwards and inwards decreasing the space in the chest cavity this increases the air pressure inside the lungs and forces the air out of the lungs.
When the internal intercostal muscles contract and diaphragm relax the ribs move downward and inward and diaphragm becomes convex dome shaped thus decreasing the volume of thoracic cavity and increasing the pressure inside as compared to the atmospheric pressure outside. A the diaphragm moves into the thoracic cavity and generates a positive pressure in the thorax relative to the atmosphere. Kg is fired from the middle of the plate making an angle.
This is a controlled process that increases the air in the lungs to reach a higher pressure than the atmospheric pressure outside which encourages it to move out. During EXPIRATION the intra-alveolar pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure. During pulmonary ventilation relaxation of the diaphragm and external intercostals ________ and air flows out of the lungs.
The diaphragm becomes contracts during the process of inspiration and relaxes during expiration. During expiration which best describes the role of the diaphragm.

Description Of Muscles Used In Breathing Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy Physiology
Mechanics Of Breathing Inspiration Expiration Teachmephysiology
0 Comments